Social Security Planning
Social Security Planning: A Step-by-Step Guide to Maximizing Your Retirement Benefits
Social Security is a cornerstone of retirement planning for millions of Americans, yet many people aren’t fully aware of the best strategies to maximize their benefits. Deciding when and how to claim Social Security can significantly impact your retirement income, so it’s crucial to approach this decision thoughtfully. Whether you’re just beginning to plan for retirement or are about to start collecting benefits, understanding the key steps can help you make the most of your Social Security income.
Step 1: Understand Your Social Security Benefits
Before you can optimize your Social Security benefits, it's important to understand how the system works:
- Eligibility Requirements: To qualify for Social Security, you generally need 40 credits, which equates to about 10 years of work. Your benefit amount is calculated based on your 35 highest-earning years.
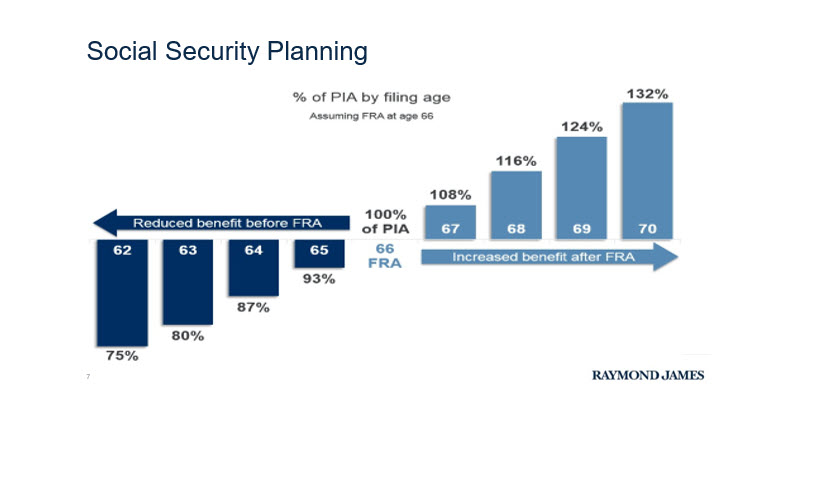
- Full Retirement Age (FRA): Your FRA is the age at which you can receive 100% of your Social Security benefits. This age varies between 66 and 67, depending on the year you were born. Knowing your FRA is essential because claiming benefits before or after this age affects your monthly payout.
Step 2: Determine the Optimal Time to Claim Benefits
The timing of when you start claiming Social Security is one of the most important decisions in your retirement planning:
- Claiming Early (Age 62): You can start receiving benefits as early as 62, but your monthly payments will be reduced by up to 30% compared to waiting until your FRA.
- Waiting Until Full Retirement Age (FRA): Claiming at your FRA means you receive your full benefit amount, which is the most straightforward approach for many.
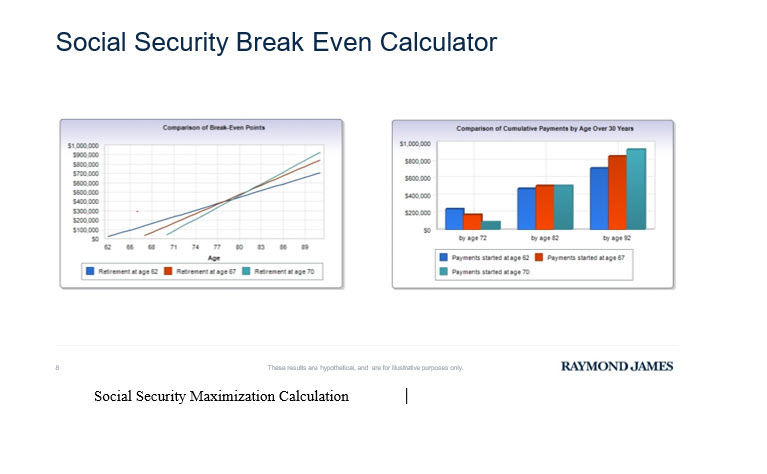
- Delaying Beyond FRA (Up to Age 70): If you delay claiming Social Security beyond your FRA, your benefit increases by about 8% per year until age 70. This strategy can significantly boost your monthly income.
Considerations:
- Longevity: If you have a longer-than-average life expectancy, delaying benefits could increase your total lifetime payout.
- Health: If you’re in good health and have a family history of longevity, delaying benefits might be beneficial.
- Income Needs: Consider whether you need the income now or if you can afford to wait to maximize your payout.
Case Study: Jane’s Decision to Delay Benefits
Jane, a 62-year-old teacher, had the option to start collecting Social Security immediately. However, after estimating her benefits, she realized that claiming at 62 would reduce her monthly benefit from $2,500 to $1,750. Instead, Jane decided to continue working part-time and wait until she reached 70 to claim benefits. By doing so, her monthly benefit increased to $3,300—a 32% boost. This decision provided her with a higher income for the rest of her life, allowing her to maintain a more comfortable retirement.
Step 3: Explore Spousal and Survivor Benefits
Social Security offers significant benefits for married couples, including spousal and survivor benefits:
- Spousal Benefits: If you’re married, you might be eligible to claim a benefit based on your spouse’s earnings record, which can be as much as 50% of their benefit at their FRA. This option is especially beneficial if your earnings were significantly lower than your spouse’s.
- Survivor Benefits: If your spouse passes away, you may be eligible to receive their full benefit amount. Planning for survivor benefits is crucial, particularly if there is a significant difference in earnings between spouses.
Step 4: Plan for the Taxation of Social Security Benefits
Many retirees are surprised to learn that Social Security benefits may be taxable. Understanding how your benefits will be taxed can help you plan more effectively:
- Income Thresholds: If your combined income (including your adjusted gross income, non-taxable interest, and half of your Social Security benefits) exceeds certain thresholds, up to 85% of your benefits could be subject to federal income tax.
- Tax Strategies: To minimize taxes, consider coordinating your Social Security benefits with withdrawals from tax-deferred accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs. Strategic withdrawals can help keep your income below certain thresholds, reducing the tax burden on your benefits.
Conclusion
Maximizing your Social Security benefits requires careful planning and strategic decision-making. By understanding your benefits, determining the best time to claim them, exploring spousal and survivor benefits, and planning for taxes, you can enhance your retirement income and secure a more comfortable future. Whether you're nearing retirement or still a few years away, taking these steps now can make a significant difference in your financial well-being.
Opinions expressed in the attached article are those of the author/speaker and are not necessarily those of Raymond James. All opinions are as of this date and are subject to change without notice. Every investor situation is unique and you should consider your investment goals, risk tolerance and time horizon before making any investment. While we are familiar with the tax provisions of the issues presented herein, as financial advisors of Raymond James, we are not qualified to render advice on legal or tax matters. You should discuss tax or legal matters with the appropriate professional.


